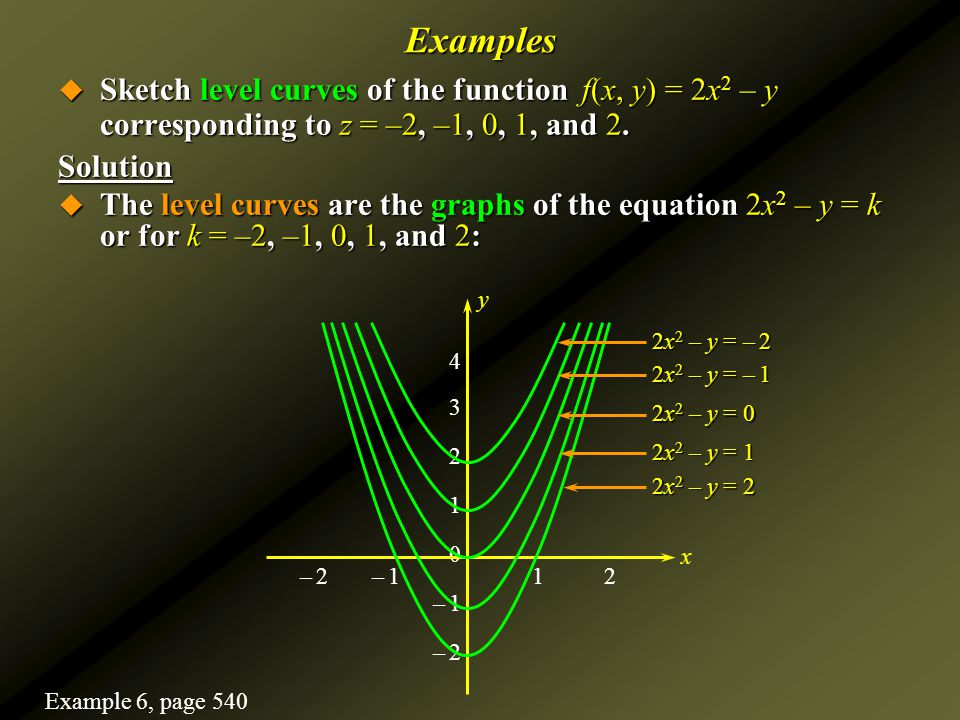
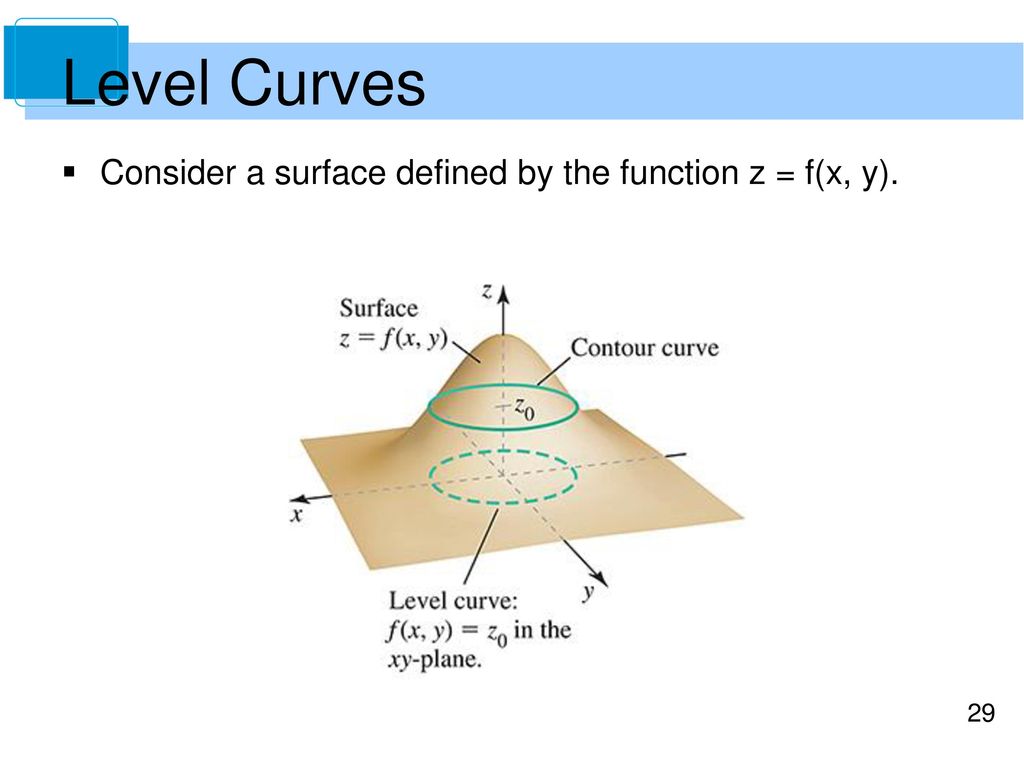
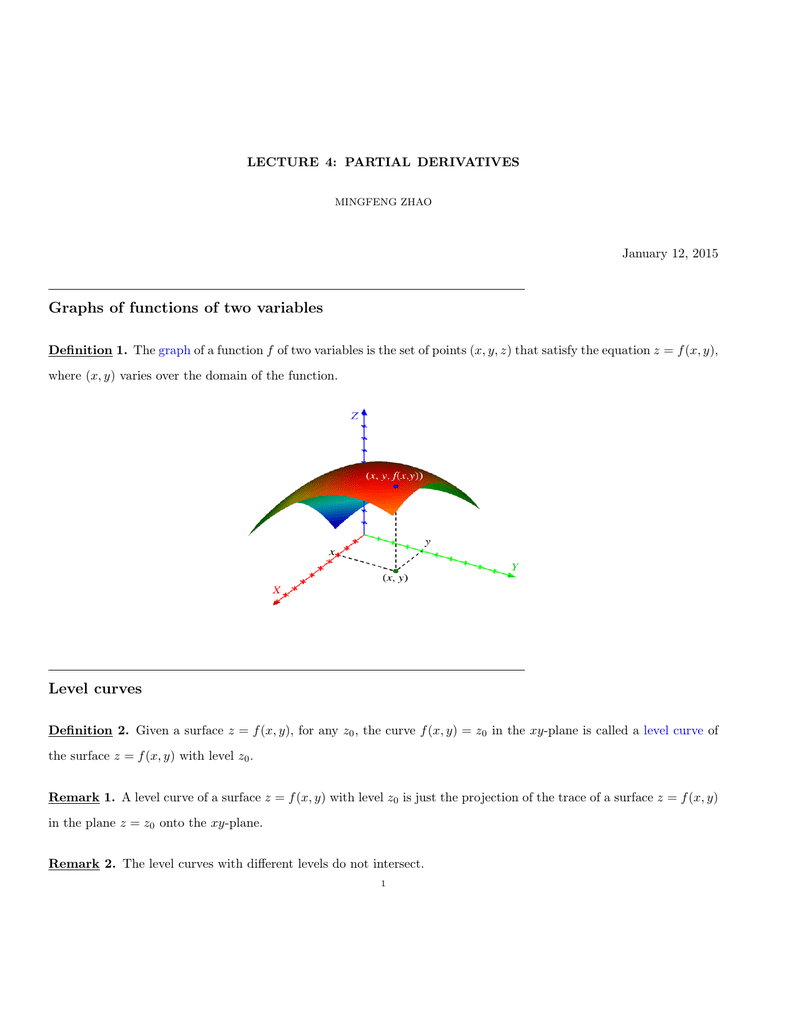
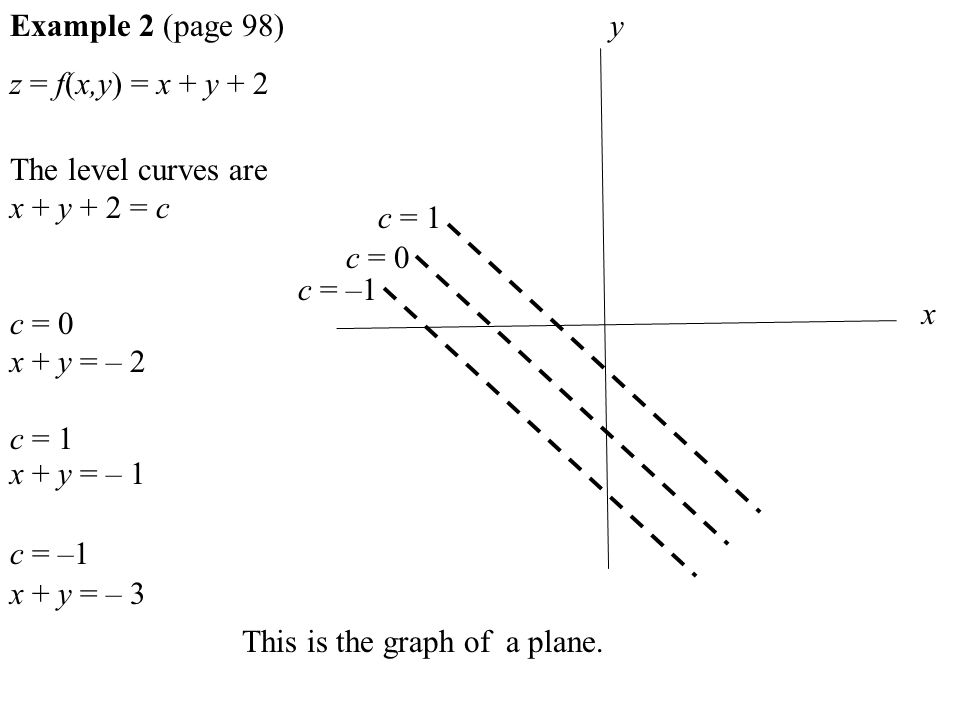
Zxy Level Curves
Draw the 3-D graph and level curves for the function f (,.
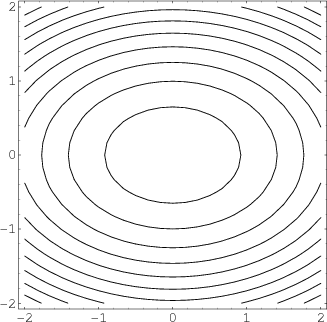
Zxy level curves. The z-axis is stretched to give a better view. A collection of equally spaced concentric circles B. The bottom of the bowl lies at the origin.
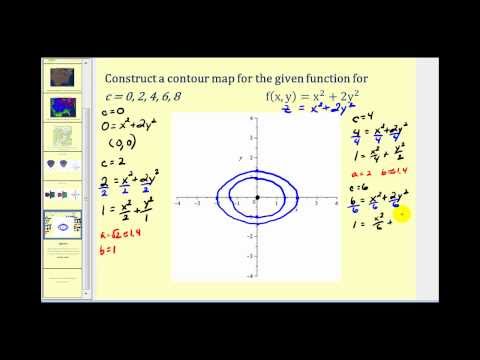
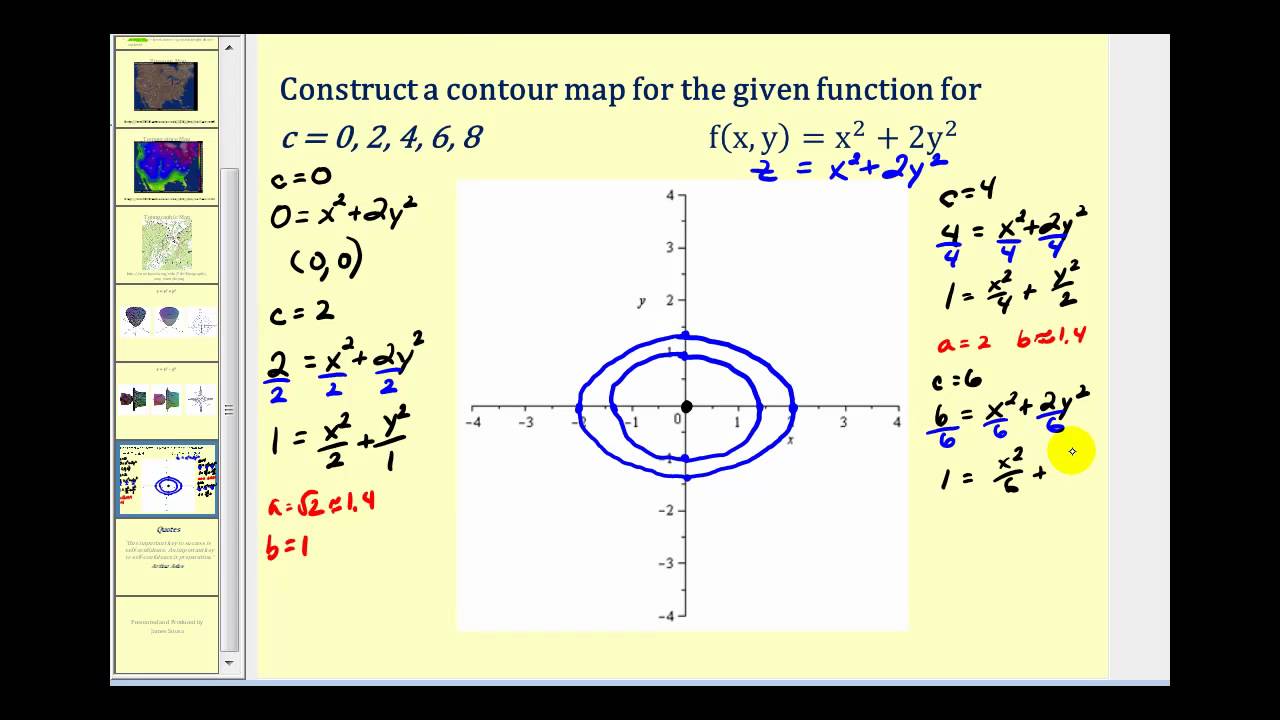
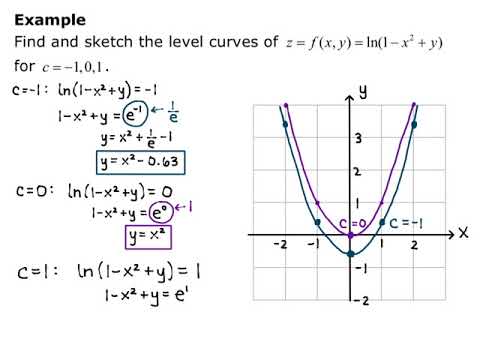
Y x 0 is the domain. Example 3 (f(x,y) = x2 +4y2 − 2x+2) Sketch the level curves of f(x,y) = x2 +4y2 −2x+2. The family of level sets can be obtained by setting f(x;y) = k, that is, p 1 x2 2y2 = k(0 k 1).
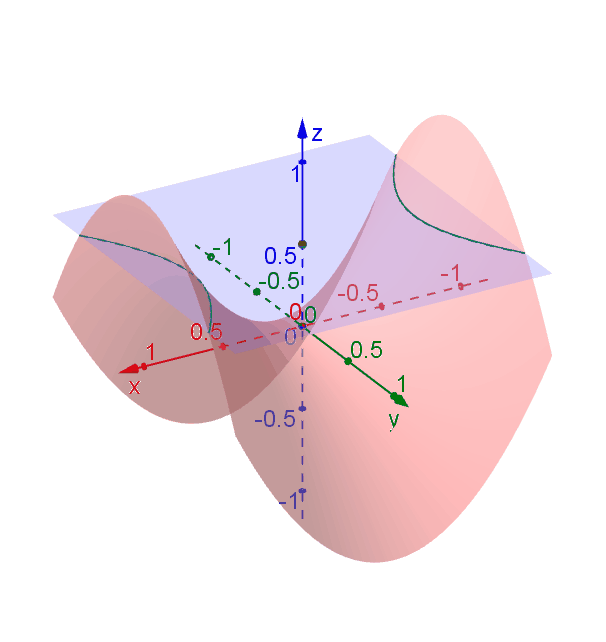
In the case of z = x y the surface has a saddle point at (0, 0). Z=y(y^2-x^2) Here is another nice cubic equation:. A collection of concentric ellipses F.
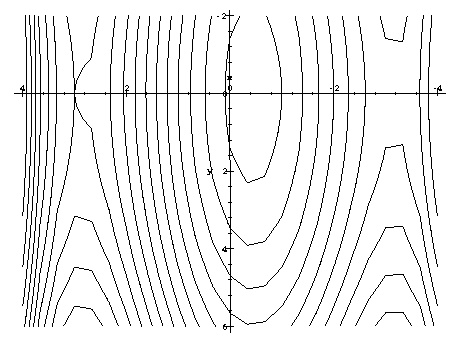
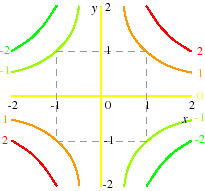
Sketch the level curves for z = xy. 1 −1 2 2 z = 3 − z = −3. The function z = ¨ xy ¨ In17:= Plot3D@Abs@xyD, 8x,-1, 1<, 8y,-1, 1<, BoxRatios-> Automatic, PlotPoints-> 30, Mesh-> False, AxesLabel-> 8"x","y","z"<D;-1-0.5 0 0.5 1 x-1-0.5 0 0.5 1 y 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 z What are the level curves?.
1, z = V(25-x2-y2) 3, z = x2 +y2 5, z =xy 6, z = 2x2 +3y2 7. A contour map of a function f(x,y) is a 2-dimensional graph showing several level curves corresponding to several values of c. Thus, in three dimensions, one would hope that the gradient is orthogonal to the level surfaces.
The range of the function is 0;1). The flat surface of z = 2x + 2y rises at an angle as z increases. Graph 3D functions, plot surfaces, construct solids and much more!.
K with the surface defined by f. F A to some element in. David Jordan View the complete course:.
(4) Find a unit vector in the direction in which fincreases most rapidly at the point P, and nd the rate of change of fat Pin that. A) write a general expression for the slope of the curve b) find the coordinates of the points on the curve where the tangents are vertical. The level curve de ned by f(x;y) = 0 is And the level curve de ned by f(x;y) = 4 is Notice that the cross-sections lie in the space of R3, while the level curves in R2.
Contour or level curve. Note again that the origin is not actually part of the domain of f. Find the level curves of the function f(x;y) = p 1 x2 2y2.
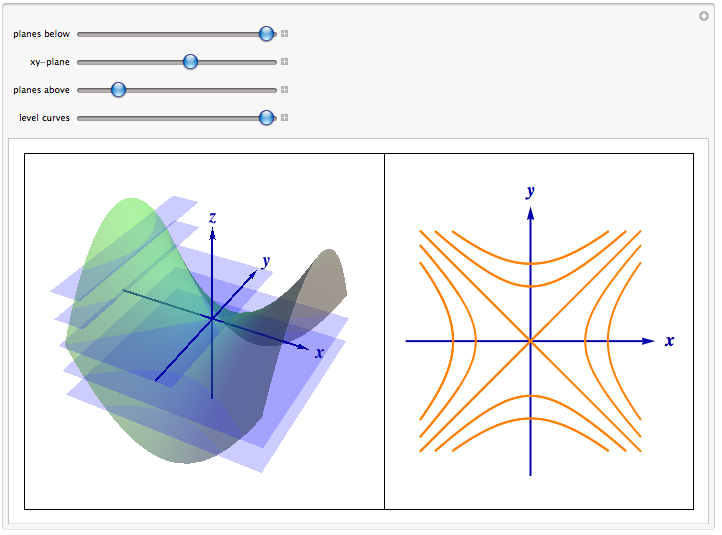
X y) = x2 − y The orientation on the left shows a hint of the parabolic nature of the surface, which becomes clearer in the rotation. The dimension that varies must be the opposite of the dimension that varies in Y. In this way, the figure demonstrates the correspondence between the level curve plot and the graph of the function.
C) at the point (0,3) find the rate of change in the slope of the curve with respect to x. Z (0,0) → 0 (1,1) → 2 (1.5,1) → 2.26 (1,1.5) → 2.55 (1.5,1.5) → 2. (2,2) → 3.73. This demo allows you to enter a mathematical expression in terms of x and y.
In12:= ContourPlot@Abs@xyD, 8x,-1, 1<, 8y,-1, 1<, PlotPoints-> 60D;-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1-1-0.5. Don't confuse the level surfaces (i.e., the level curves) with the surface defined by z = f (x, y). (a) Maximize z = xy Constraint:.
The following are the level curves. A level curve of \(f(x,y)\) is a curve on the domain that satisfies \(f(x,y) = k\). Free online 3D grapher from GeoGebra:.
A collection of unequally spaced concentric circles C. Curves on surfaces, to constructthe natural flow for images A geodesic curve is a curve along which the geodesic on surfaces. Contour graphs (curves) are made by intersecting the surface with the planes z=Constant for various constants.
As the plot shows, the gradient vector at (x,y) is normal to the level curve through (x. Here is a sketch of the level. (a) Suppose f(900,14,30.
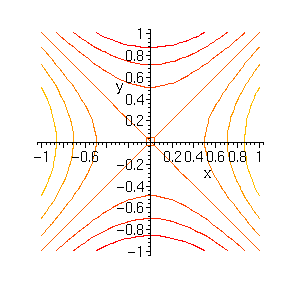
Z = xy. When drawing in three dimensions is inconvenient, a contour map is a useful alternative for representing functions with a two-dimensional input and a one-dimensional output. X-coordinates, specified as a matrix the same size as Z, or as a vector with length n, where m,n = size(Z).The default value of X is the vector (1:n).
Example 2 Determine the surface area of the part of \(z = xy\) that lies in the cylinder given by \({x^2} + {y^2} = 1\). If the positive y -axis is North and the positive x -axis is East then the terrain rises to the northeast and southwest and declines to the southeast and the northwest. We will plot the level curves by substituting z value with a constant.
If you think of the graph z = x y as a surface "hovering" over the x - y plane, then when you say c = x y, this would trace in the x - y plane a curve denoting that the point "above" (in the sense the points in the hovering surface) are exactly at height c. It can be viewed as the intersection of the surface \(z = f(x,y)\) and the horizontal plane \(z = k\) projected onto the domain. A collection of unequally spaced parallel lines E.
Use the graph to approximate the indicated extrema. A level curve can be described as the intersection of the horizontal plane z =. For k= 0, we simply get f(x;y) = 0 )x= 0, i.e, the y-axis.-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 x-0.8-0.6-0.4.
On the topographical map below, the level curves for the height function h(x, y) are marked (in meters);. The following diagrams shows how the level curves \f(x,y. Z = 1/(x - 1).
Fix any real number C. Where T is measured in °C and x, y, z in meters. A scale is given.
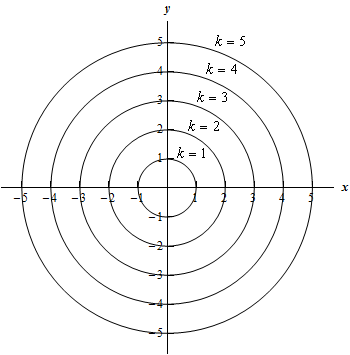
EX 5 Graph gradient vectors and level curves for. (These are usually equally spaced values.). K, where k is a constant in the range of f.
The X, Y, and Z axes are where they are for illustration purposes only. Because it is a curve in 2d, it is usually easier to sketch than the graph of f. Y is a two-dimensional curve with the equation f x ,.
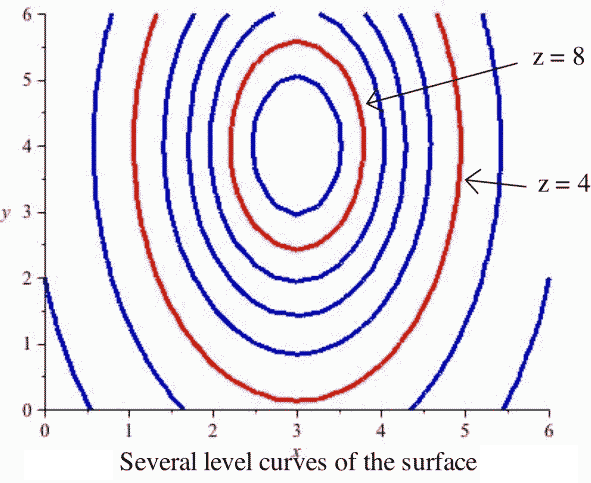
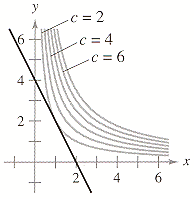
In Fig-ure 16.1.2(a) the contours corresponding to c= 2, 4, 6, 0, 2, 4, 6 are shown. The level curves of $f(x,y)$ are curves in the $xy$-plane along which $f$ has a constant value. A collection of equally spaced parallel lines B.
When X is a matrix, the values must be strictly increasing or decreasing along one dimension and remain constant along the other dimension. When you drag the green point to the right, each level curve $f(x,y)=c$ moves to the height $z=c$, so that they are in the same position as in the graph of $z=f(x,y)$. X + y - 4 = 0.
1/28/14 9:29:40 PM. This is because we think of level curves as subsets of the domain corresponding to a function value. The monthly mortgage payment in dollars, P, for a house is a function of three variables P = f(A,r,N) where A is the amount borrowed in dollars, r is the interest rate, and N is the number of years before the mortgage is paid off.
(1 point) Match the surfaces with the verbal description of the level curves by placing the letter of the verbal description to the left of the number of the surface. A collection of unequally spaced concentric circles C. – John Wayland Bales Jul 18 '17 at 23:22.
In two dimensions, the gradient was orthogonal to the level curves. Sketch a vector pointing in the direction of the gradient of h:. (a) Find the rate of change of temperature at the point P(2, − 1, 2) in the direction toward the point (3, −3, 3).
A level curve of the surface z =. Contour lines can be a bit difficult to understand, so if you are having trouble, you may find the 3D surface plotter useful to help visualise the actual shape of the 3D surface. (b) (1 credit ) Mark on the map a point Q at which h.
The level curves are parabolas opening to the right (see video for sketch). The graphs show the constraint and several level curves of the objective function. Hence when 0 k<1, the level sets are ellipses.
Contour lines are another name for level curves. Here is the surface z = xy with jxj • 1 and jyj • 1. Level curves are two-dimensional curves parallel to the xy plane.
Natural link between level sets and the image evolution, of the curve according to s, and N is the normal to the and the nice properties of the geodesic curvature flow of surface;. Match the surfaces with the verbal description of the level curves by placing the letter of the verbal description to the left of the number of the surface. (a) f(x;y) = p y x Solution:.
(3) Sketch the level curve of f(x;y) = x2 + 4y2 that passes through the point P( 2;0) and draw the gradient vector at P. 2 x + y = 4 (b) Minimize z = x 2 + y 2 Constraint:. This is a closed set.
The level curves here have the form z = c for a constant c, and the level curves are (in general) one-dimensional—they are lines or curves. 4.Describe the level surfaces of f(x;y;z) = 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 3z A family of spheres with center (0;0;0). Adjacent level curves represent a di erence of 100 meters in height.
Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://o. For the function z = xy, the contours are hyperbolas xy = c. Fall 10 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:.
Finally, determine if the domain is open, closed, or neither. Then, for the specified function f, the level curve. Then sketch at least three non-empty level curves of each function.
If you know of a really cool 3D function that you would like to send to me, I could add it here and put it up as the 3D surface curve of the month. (b) In which direction does the temperature increase fastest at P?. Many newspapers publish a daily map showing the temperature throughout the nation with the aid of contour lines.
Figure 16.1.2(b) is an example. Level curves are also known as contour lines. Z=xy(y^2-1) The contour lines are drawn on the surface then lifted up straight up to a plane and then shown flat in small window on the right hand side.
A collection of equally spaced parallel lines D. Match the surfaces with the verbal description of the level curves by placing the letter of the verbal description to the left of the number of the surface. Such ideas are seen in university mathematics and pr.
The level curves make it obvious. Show Solution In this case we are looking for the surface area of the part of \(z = xy\) where \(\left( {x,y} \right)\) comes from the disk of radius 1 centered at the origin since that is the region that will lie inside the. Find more Mathematics widgets in Wolfram|Alpha.
We square both sides and after a simple algebra we can obtain x2 + 2y2 = 1 k2. Z = 2x + 3y A. Level curve (surface) of f through P.
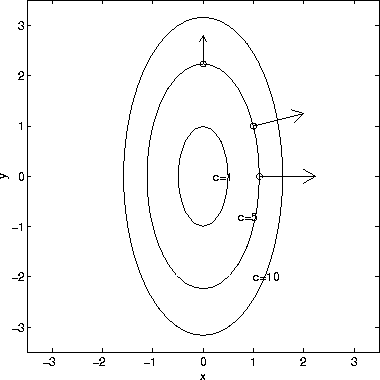
The figure below shows the level curves, defined by f(x,y)=c, of the surface. Scroll down to the bottom to view the interactive graph. The points on the level curve are points where the function takes the value c.
The level curve through P( 2;0) is the ellipse x 2+ 4y2 = 4 or (x=2) + y2 = 1. When k= 1, x2 + 2y2 = 0 and hence the level set is a. Graph and explore the rectangle area function z = xy.
(a) (1 credit ) At the point P;. The temperature at a point (x, y, z) is given byT(x, y, z) = 0 e − x 2 − 3 y 2 − 9 z 2. More information about applet.
The gradient vector <8x,2y> is plotted at the 3 points (sqrt(1.25),0), (1,1), (0,sqrt(5)). Make a sketch of the level curves for the function f(x;y) = xy. We label each curve by the value of the constant.
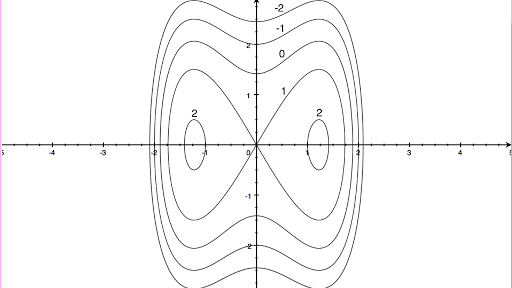
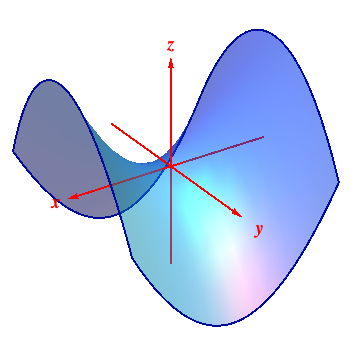
Here is the Monkey Saddle:. The graph “standard” orientation of the x-y-z axes is on the left, and a rotation of the graph on. Y z = −3 z = 3 −2 2 −1 1 0 x.
When you hit the calculate button, the demo will calculate the value of the expression over the x and y ranges provided and then plot the result as a surface. MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02SC Multivariable Calculus Fall 10 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:. Wolfram|Alpha brings expert-level knowledge and capabilities to the broadest possible range of people—spanning all professions and education levels.
The level curves are the ellipses 4x^2+y^2=c. This consists of all points in the plane above or on the line y = x. Here are a couple of examples.
Each level curve on the grid represents a different value for z. Z z = xy f (x) = y = … Example F:. Etc… Recall that a function from set A to set B is a rule that maps each element of.
Thus, in three dimensions, one would hope that the gradient is orthogonal to the level surfaces. Sketch the level curve z = k for z = x y,k = −2,−1,0,1,2. The level curves are hyperbolas xy = constant.
Mathematicians would switch the Y and Z axes with each other. A collection of concentric ellipses. Sketch the level curves for z = 10, 8, 6, 4, 2.
Those are the level surfaces here, not the surface z = f (x, y). The level curves for f(x,y) lie in the xy-plane. The level curves of fare therefore just circles centered at di erent points on the x-axis and passing through the origin.
Get the free "Contour Plot" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle.

14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts
Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet
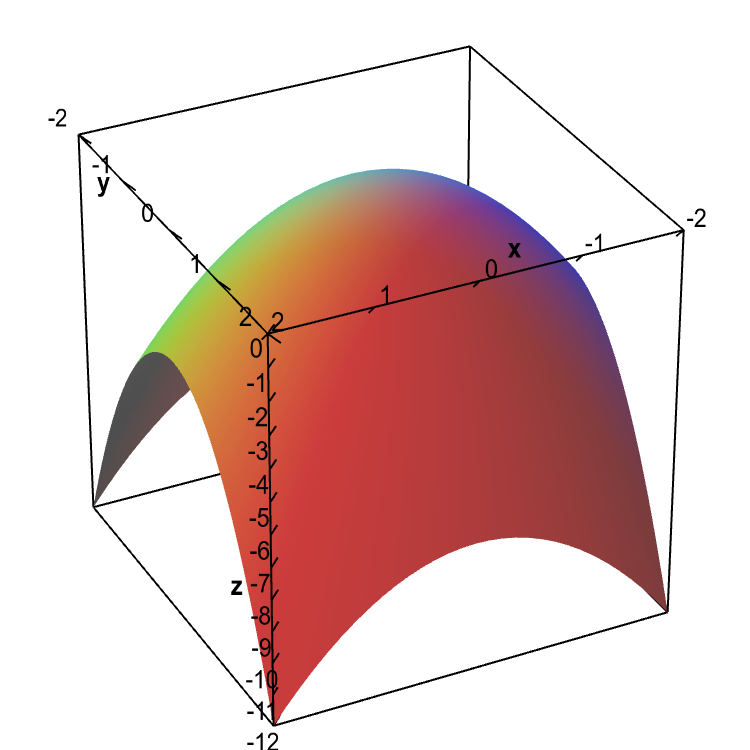
Level Sets Math Insight
Zxy Level Curves のギャラリー
8 Calculus Of Several Variables Functions Of Several Variables Ppt Download
16 8 Lagrange Multipliers
Level Sets Math Insight
2

Solved The Picture Shows A Number Of Level Curves Of The Chegg Com
Sketching Level Curves At Paintingvalley Com Explore Collection Of Sketching Level Curves
Math La Asu Edu Surgent Mat267 Examples Levelcurves Pdf

Graphing Level Curves For E X Functions Matlab
Introduction To Functions Of Several Variables Ppt Download

Level Curves

Graphs And Level Curves
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrvtp4 Aq Ybhrhfxubj35rpw19wmrecumqpd68xfxzeryirtaj Usqp Cau
2
Www Math Tamu Edu Glahodny Math251 Section 12 1 Pdf

Calculus Iii
2
2

Jl Chapter Partial Derivatives 13
The Gradient And Directional Derivative
Http Www Math Utah Edu Golden Courses 2210 2210 P2 F19 Pdf
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqcwypej7hlxxlinxuwu0le2pata7a9nlcpjvny0ax4m5f5zfsh Usqp Cau
4 1 Functions Of Several Variables Calculus Volume 3 Openstax

Level Curves
2

Contour Map Of F X Y 1 X 2 Y 2 Youtube
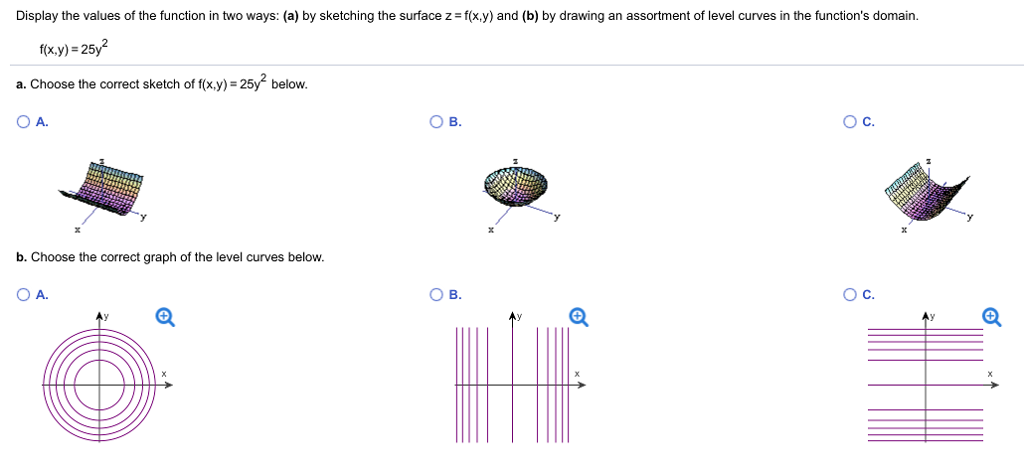
Solved Display The Values Of The Function In Two Ways A Chegg Com

Level Curves And Graphs Homeworklib

Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
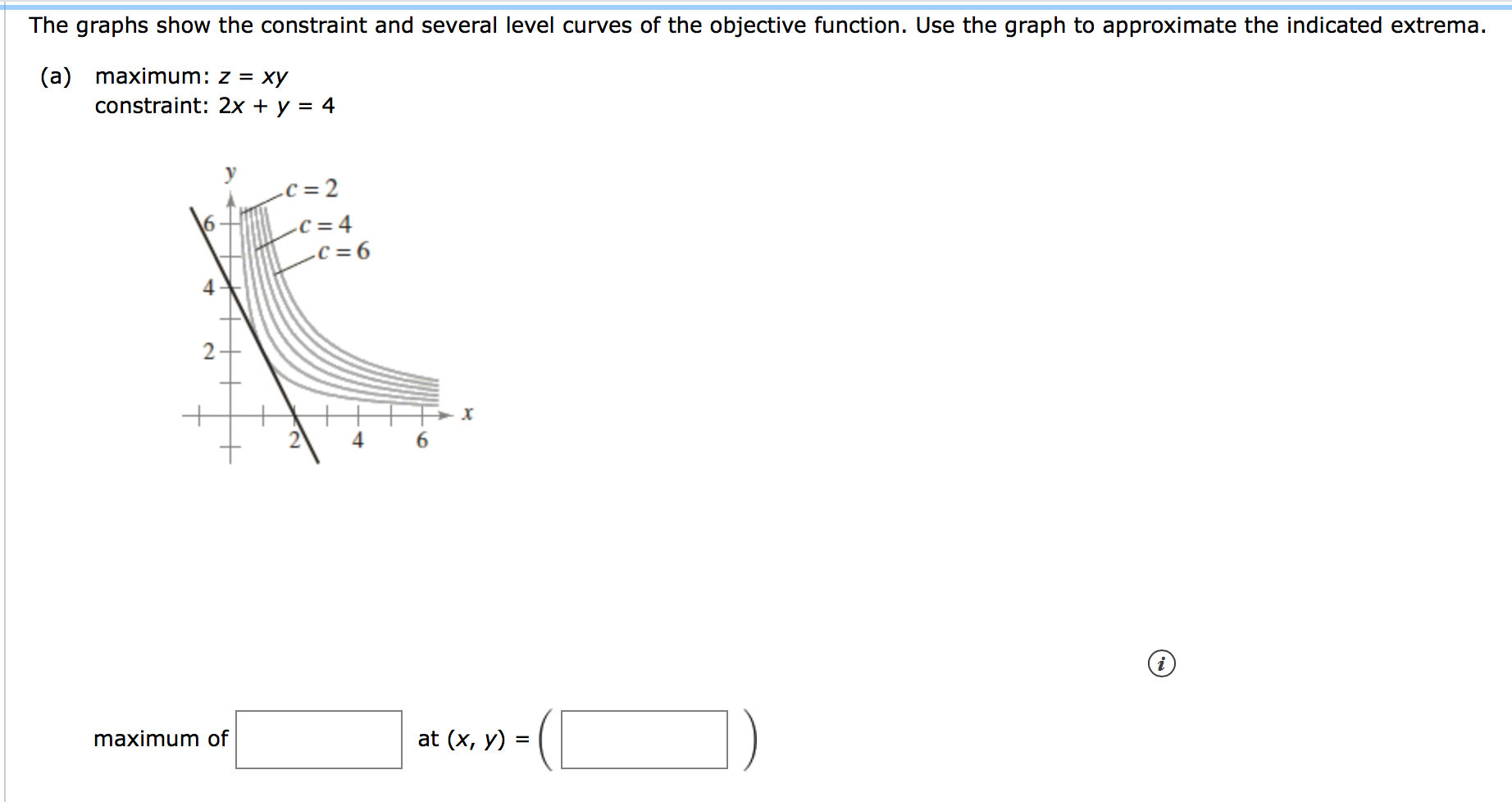
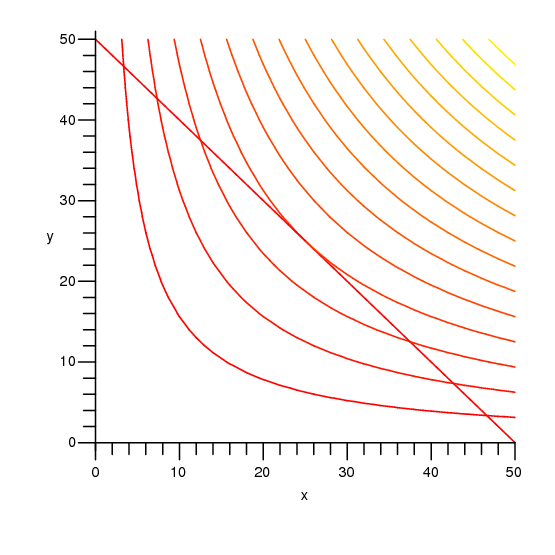
Answered The Graphs Show The Constraint And Bartleby

Solved 4 The Level Curves Of Z Tx Y Are Shown In Fig 1 Chegg Com
Contour Maps Article Khan Academy

Matlab Tutorial

Level Curves Of Functions Of Two Variables Youtube

Domain Multivariable Solved Quiz Docsity
Graphs Of Functions Of Two Variables
Business Calculus
Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables
Level Curves Of Functions Of Two Variables Youtube

Implicit Curve Wikipedia
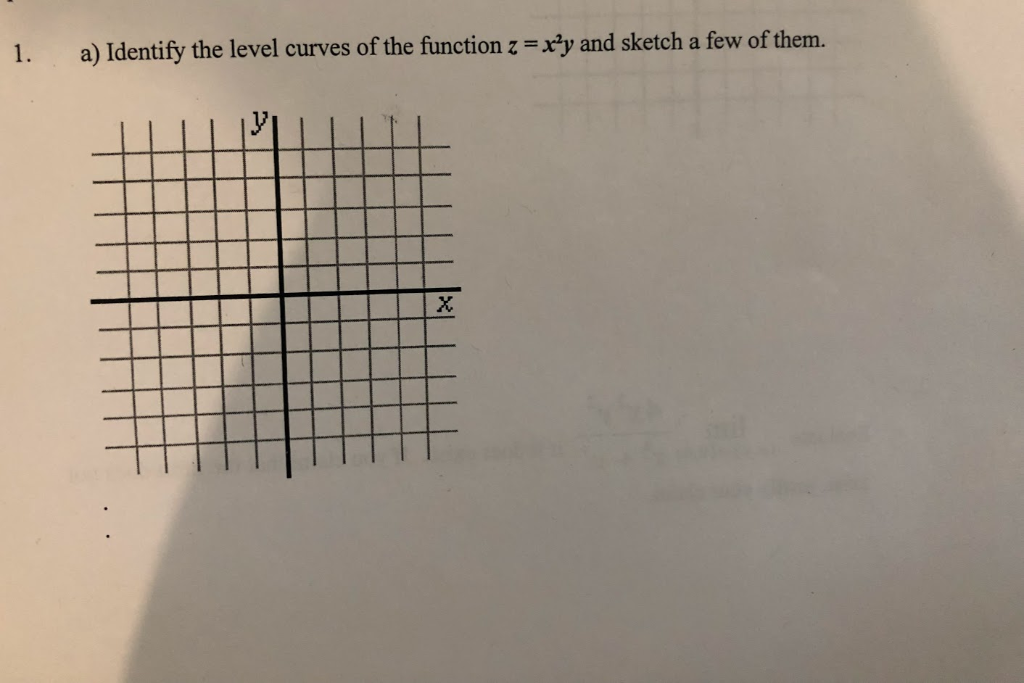
Solved A Identify The Level Curves Of The Function Z Xy Chegg Com
Http Homepages Math Uic Edu Apsward Math210 12 2
Partial Derivatives

Problem On A Path Of Steepest Descent Leading Lesson
The Study Economics For Ma Ignou Microeconomics Macroeconomics Econometrics Mathmatical Economics Graphical Representation Of Functions
Level Curves

Solved Identify The Constraint And Level Curves Of The Ob Chegg Com

Answered Explain How To Graph The Level Curves Bartleby
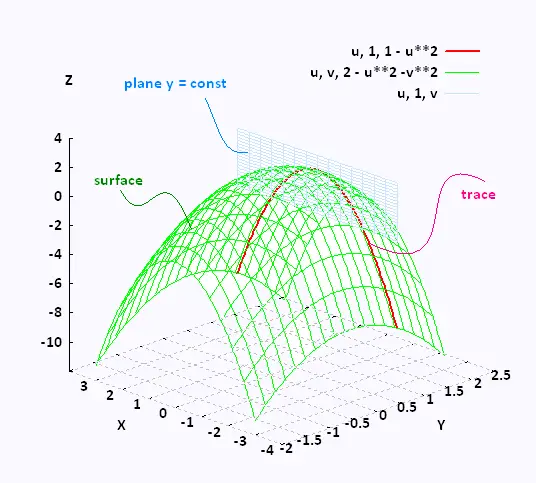
Mathematics Calculus Iii
Surfaces And Traces

Final Study Guide Please Help 1 Sketch The Indicated Level Curves Of The Following Functions 0 Z 2 And Z 4 Level Curves Of F X Y Huz The Z 2 Z
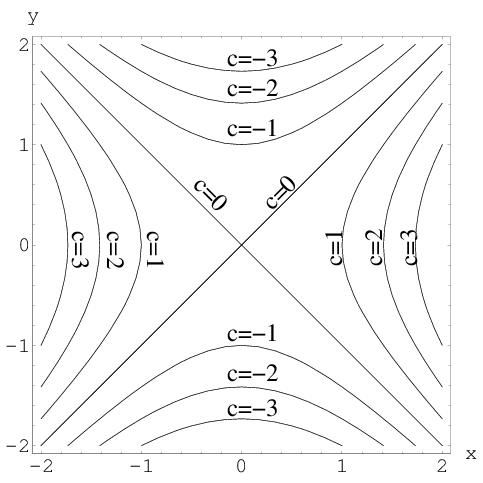
Level Set Examples Math Insight

Seminar Assignments Section 14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Studocu
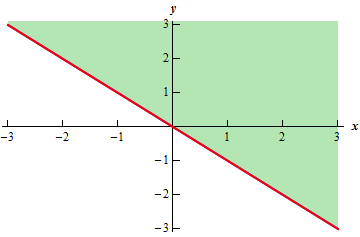
Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables
Q Tbn 3aand9gctkz76j2iwtb7wknyqeq1nfgwzal3cgzu5i8f 53axwud0f4hq1 Usqp Cau
If X X1 X2 Represents A Point In A Subset A Of Rn And F X Is Exactly One Point In Rm Then We Say That F

Examples Wednesday Feb 19
Relief Functions And Level Curves

Solved Identify The Constraint And Level Curves Of The Objective Function Shown In The Figure Use The Figure To Approximate The Indicated Extrema Assuming That X And Y Are Positive Maximize Z
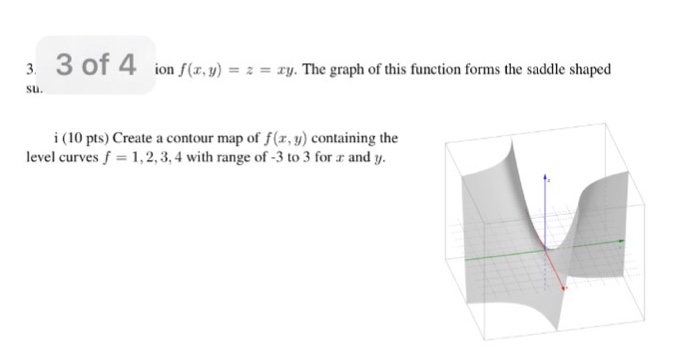
Solved F X Y Z Xy The Graph Of This Function Forms Chegg Com
Math La Asu Edu Surgent Mat267 Examples Levelcurves Pdf
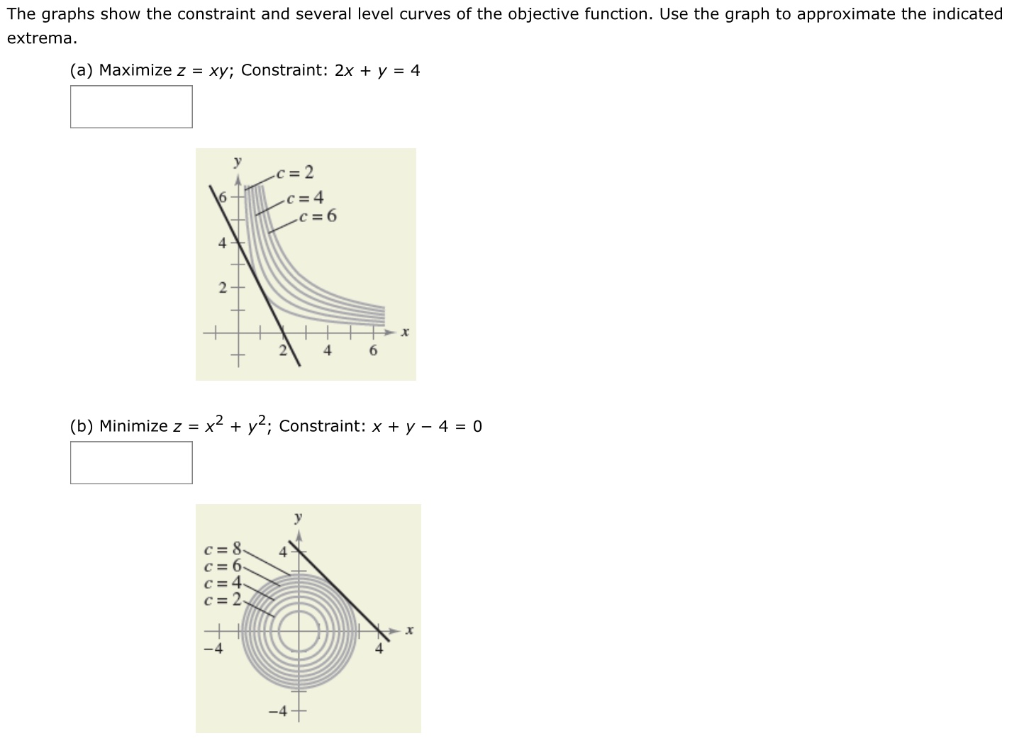
Solved The Graphs Show The Constraint And Several Level C Chegg Com
Www Math Ucdavis Edu Zekius S12mat16c Hw Worksheet3 Pdf
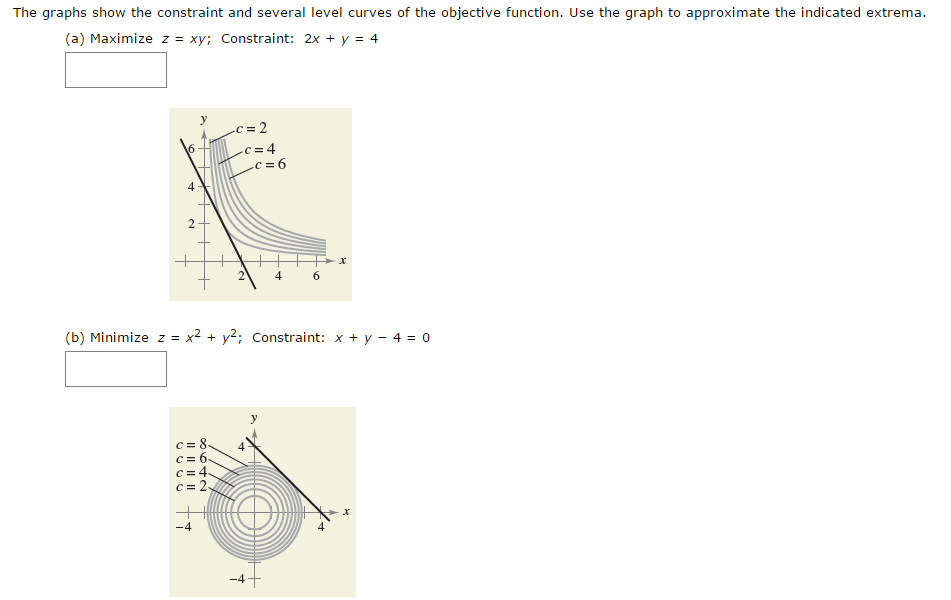
Solved The Graphs Show The Constraint And Several Level C Chegg Com

Gradients And Level Curves
Section 13 1 Level Curves Youtube

Graphing Level Curves Mathematics Stack Exchange
Multivariable Functions Level Curves And Partial Derivatives
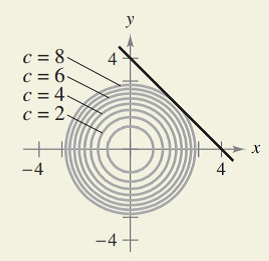
How Do You See It The Graphs Show The Constraint And Several Level Curves Of The Objective Function Use The Graph To Approximate The Indicated Extrema A Maximize Z Xy Constraint
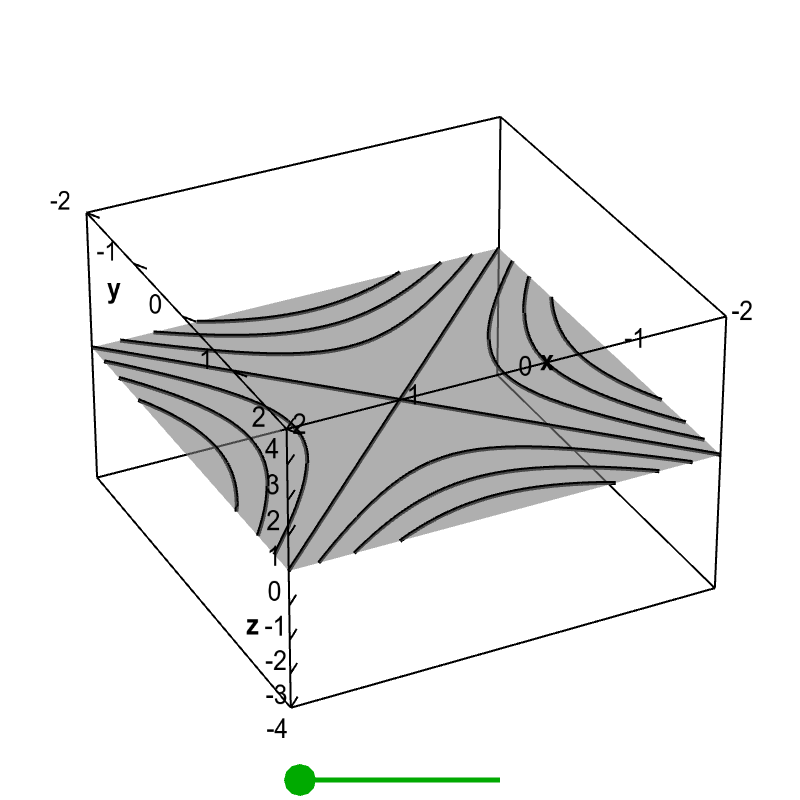
Level Set Examples Math Insight

Math 15 Lecture 7 Level Curves And Contour Plots Oneclass
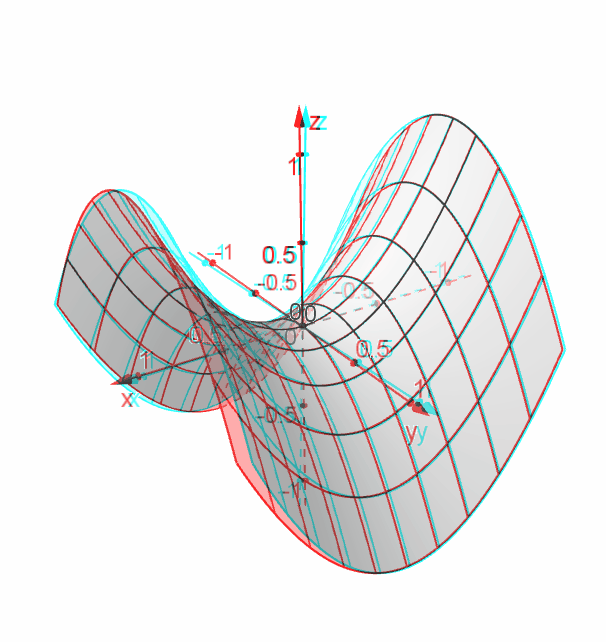
Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet
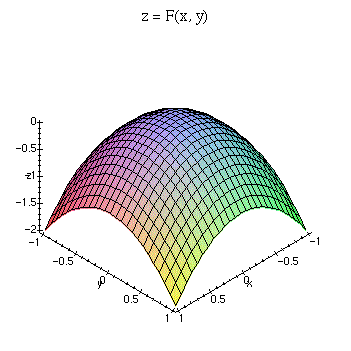
Relief Functions And Level Curves
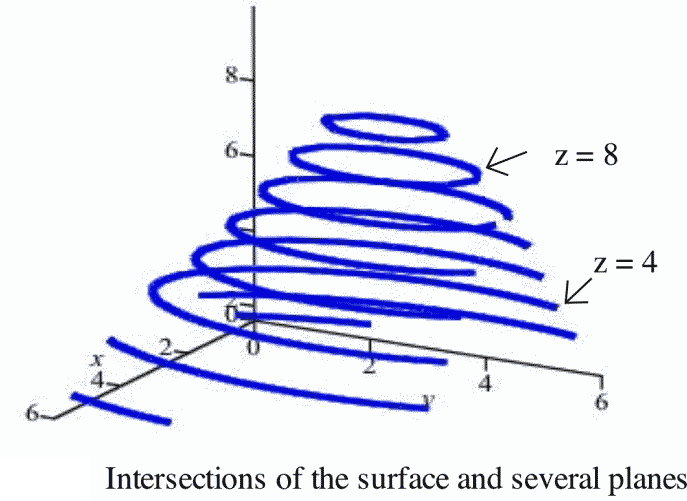
Business Calculus

Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Is A Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gctggdb5gd0wu Mlom Olvadtiewztthamycis51inb8rdx5r5ov Usqp Cau

The Graphs Show The Constraint And Several Level Curves Of The Objective Function Use The Graph Homeworklib
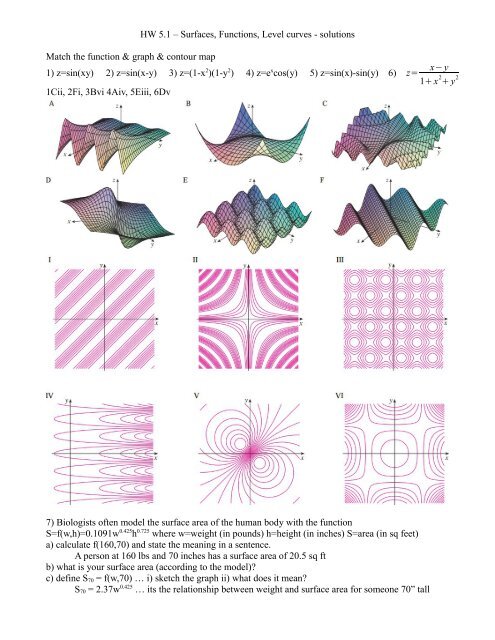
Hw 5 1 A Surfaces Functions Level Curves Solutions Match The
2

Pilot Problem Set 2 As 110 2 Calculus Iii Jhu Studocu
16 8 Lagrange Multipliers

Document

Gradients And Level Curves

Level Curves

Level Curve
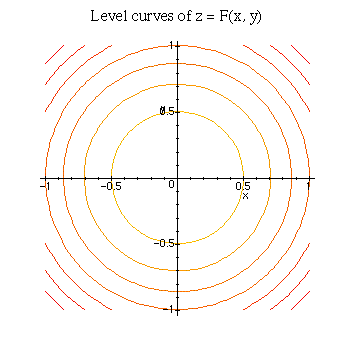
Relief Functions And Level Curves
Ocw Mit Edu Resources Res 18 001 Calculus Online Textbook Spring 05 Textbook Mitres 18 001 Strang 13 Pdf
Solved Identify The Constraint And Level Curves Of The Ob Chegg Com
2

Implicit Curve Wikipedia

Matlab Tutorial
2
Canvas Instructure Com Files Download Download Frd 1
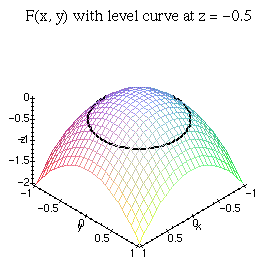
Relief Functions And Level Curves

How To Sketch Level Curves Youtube
2
4 1 Functions Of Several Variables Calculus Volume 3 Openstax

Matlab Tutorial

How To Graph The Domain Of Question 11 Calculus
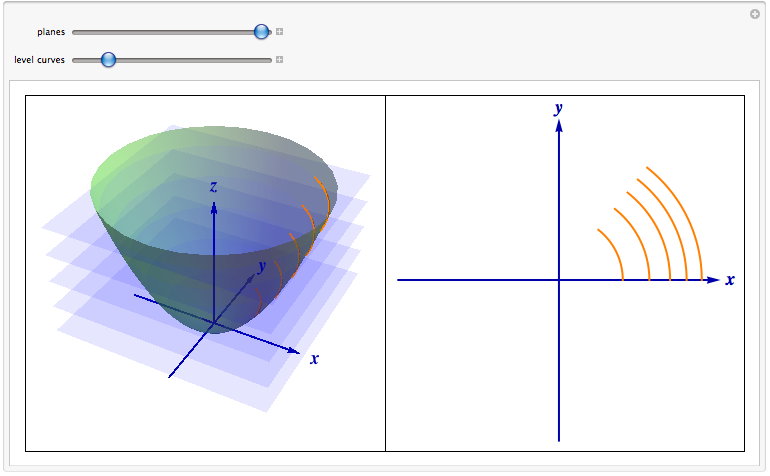
Level Curves



